Emergency Pandemic Ventilator 2020
The following material is the outcome of an experimental design project undertaken by researchers at the University of Calgary. The materials contain a theoretical approach to solving design problems. No testing has been to done to determine the safety or effectiveness of the proposed device in patient care
United through the Pandemic Ventilator Design Team Slack workspace, a team of almost 100 members has gathered to create a simple ventilator plan that can be assembled from readily available, commercial off-the-shelf materials with minimal modification. This ventilator concept is intended for use as a last resort in a catastrophically overloaded healthcare system or in a location lacking adequate resources, where the alternative is denial of ventilation due to lack of equipment and a significant probability of death.
The following material is the outcome of an experimental design project initiated by researchers at the University of Calgary. The materials contain a theoretical approach to solving design problems. No testing has been done to determine the safety or effectiveness of the proposed device in patient care.
Some recent updates:
- EPV update 2020.04.25
- EPV update 2020.04.05
- EPV update 2020.04.04
- EPV update 2020.03.31
- previous (2020.03.17 v1.6) concept document in PDF
Concept
The negative pressure ventilator is comprised of three modules (Fig. 4):
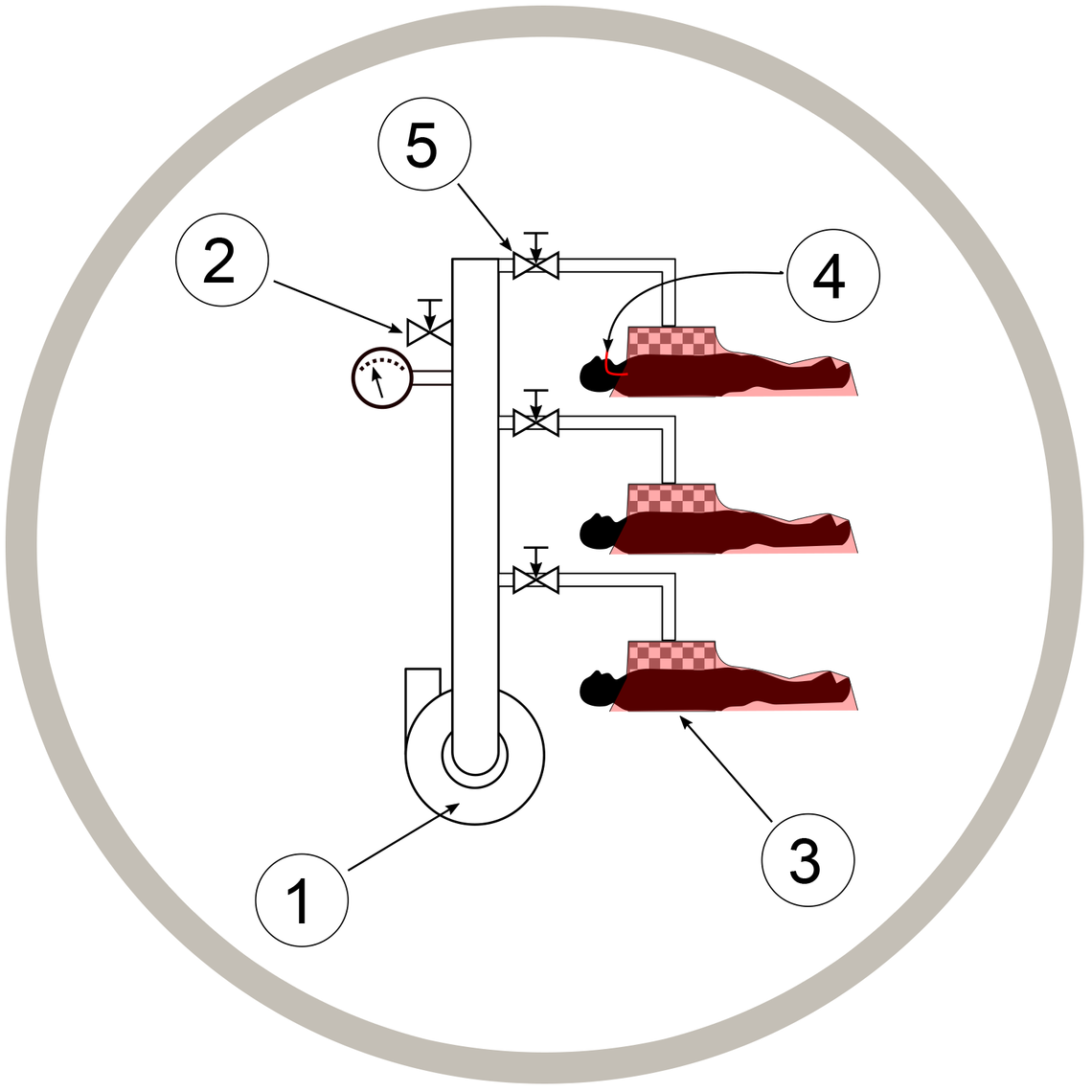
Fig. 4: Concept emergency negative-pressure ventilation system
Pressure sink (1) - in this example a central blower serves multiple patients. Ideally located away from patient (or even outside building) to reduce noise.
Redundancy and generator backup if possible. Negative pressure level set at blower and/or via bleed valve (2). Patients in jacket-type chambers (3) may be intubated (4) if necessary, to prevent airway collapse.
Valves (5) to pressure sink and room air open and close mechanically or electronically to control respiratory cycle timing and pressure.
Note that patients will be breathing (and exhaling into) room air, so contamination issues may need to be addressed. If blower exhaust is directed somewhere appropriate, the same ducting could also be used to provide removal of exhaled air.
